- Foreword
- OS Requirements
- Currently Not Supported
- Xcode
- Command Line Tools
- Homebrew
- Miniforge
- Create virtual environment
- Install Tensorflow dependencies
- Install Tensorflow
- Install metal plugin
- Install needed packages
- Test
- JupyterLab
- VSCode
- Further reading
- Reference
Foreword
A few days ago, I saw that https://github.com/apple/tensorflow_macos has been archived, and the README stated that TensorFlow v2.5 natively supports M1.
You can now leverage Apple’s tensorflow-metal PluggableDevice in TensorFlow v2.5 for accelerated training on Mac GPUs directly with Metal. Learn more here.
This article serves as an update of the Apple Silicon Mac M1/M2 Machine Learning Environment (TensorFlow, JupyterLab, VSCode), and will give you a detailed introduction to how to install the latest supported GPU Accelerated TensorFlow.
OS Requirements
- macOS 12.0+
Currently Not Supported
- Multi-GPU support
- Acceleration for Intel GPUs
- V1 TensorFlow Networks
Xcode
Install Xcode from App Store.

Command Line Tools
Install Xcode Command Line Tools by downloading it from Apple Developer or by typing:
1
catchzeng@m1 ~ % xcode-select --install
Homebrew
1
catchzeng@m1 ~ % /bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
Miniforge
Anaconda cannot run on Apple Silicon, Miniforge is used to replace it.
Download the Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64 from https://github.com/conda-forge/miniforge.
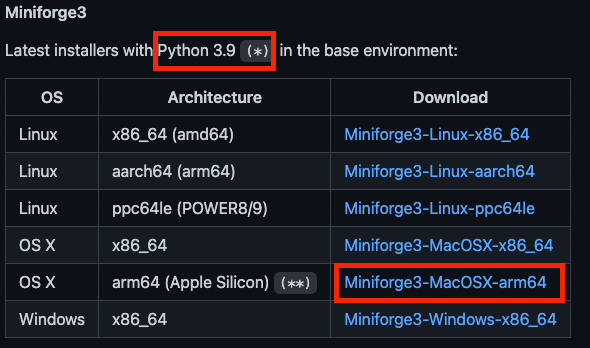
If you are using bash, execute the following command to install Miniforge
1
catchzeng@m1 ~ % bash Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64.sh
If you are using zsh, execute the following command to install Miniforge
1
catchzeng@m1 ~ % zsh Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64.sh
Restart the terminal and check it.
1
2
3
4
(base) catchzeng@m1 ~ % which python
/Users/catchzeng/miniforge3/bin/python
(base) catchzeng@m1 ~ % which pip
/Users/catchzeng/miniforge3/bin/pip
Create virtual environment
Create and activate a conda virtual environment with python 3.9.5 (as required for TensorFlow).
1
2
3
(base) catchzeng@m1 ~ % conda create -n tensorflow python=3.9.5
(base) catchzeng@m1 ~ % conda activate tensorflow
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ %
Install Tensorflow dependencies
First installation
1
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % conda install -c apple tensorflow-deps
Note: tensorflow-deps versions are following base TensorFlow versions so:
For v2.8:
For v2.10:
Upgrade installation
If you have installed v2.8 before and want to update v2.10, you can execute the following command to install.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# uninstall existing tensorflow-macos and tensorflow-metal
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % python -m pip uninstall tensorflow-macos
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % python -m pip uninstall tensorflow-metal
# Upgrade tensorflow-deps
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % conda install -c apple tensorflow-deps --force-reinstall
# or point to specific conda environment
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % conda install -c apple tensorflow-deps --force-reinstall -n tensorflow
Install Tensorflow
1
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % python -m pip install tensorflow-macos
Install metal plugin
1
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % python -m pip install tensorflow-metal
Install needed packages
1
2
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % brew install libjpeg
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % conda install -y matplotlib jupyterlab
Note: libjpeg is a required dependency for matplotlib.
Test
TensorFlow
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % python
Python 3.9.5 | packaged by conda-forge | (default, Jun 19 2021, 00:24:55)
[Clang 11.1.0 ] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import tensorflow as tf
Init Plugin
Init Graph Optimizer
Init Kernel
>>> print(tf.__version__)
2.10.0
>>>
JupyterLab
1
(tensorflow) catchzeng@m1 ~ % jupyter lab
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras import models
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
model.summary()

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
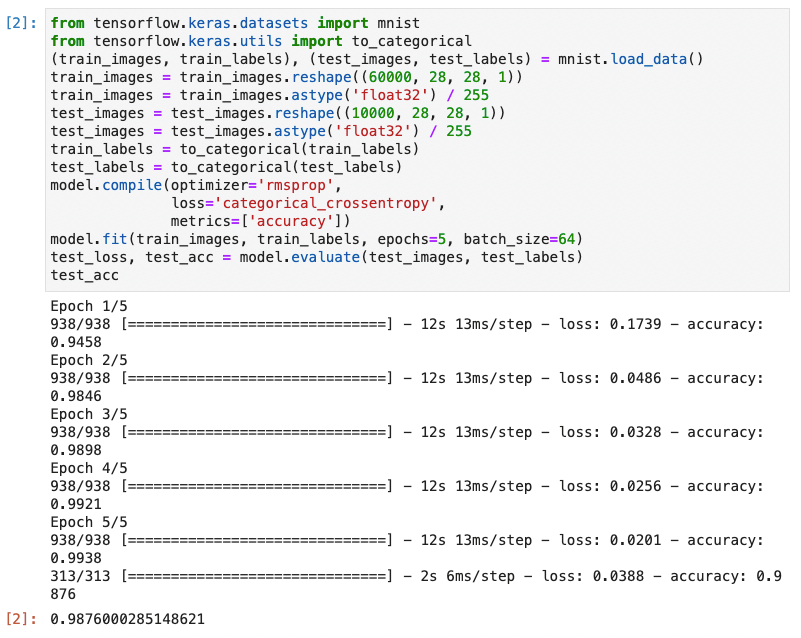
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = mnist.load_data()
train_images = train_images.reshape((60000, 28, 28, 1))
train_images = train_images.astype('float32') / 255
test_images = test_images.reshape((10000, 28, 28, 1))
test_images = test_images.astype('float32') / 255
train_labels = to_categorical(train_labels)
test_labels = to_categorical(test_labels)
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=5, batch_size=64)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels)
test_acc
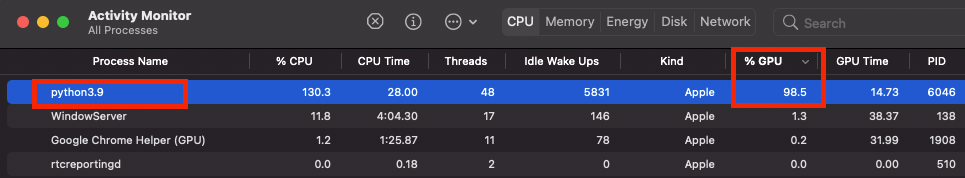
Open the Activity Monitor and you can see that Python is using GPU resources.
VSCode
Install Python support

Select virtualenv and trust the notebook

Run the notebook
Further reading
- Deep Learning (TensorFlow, JupyterLab, VSCode) on Mac
- Installing TensorFlow GPU on Ubuntu with apt
- Installing TensorFlow GPU on Win10
- Deep Learning (TensorFlow, JupyterLab, VSCode) on Apple Silicon M1 Mac

 AI - Apple Silicon Mac M1/M2 原生支持 TensorFlow 2.10 GPU 加速(tensorflow-metal PluggableDevice)
AI - Apple Silicon Mac M1/M2 原生支持 TensorFlow 2.10 GPU 加速(tensorflow-metal PluggableDevice)