注:由于 https://github.com/apple/tensorflow_macos 已经 archived,建议大家根据 Apple Silicon Mac M1/M2 原生支持 TensorFlow 2.10 GPU 加速(tensorflow-metal PluggableDevice) 安装最新支持 GPU 加速的 TensorFlow。
- Xcode
- Command Line Tools
- Homebrew
- Miniforge
- 下载 Apple TensorFlow
- 创建虚拟环境
- 安装必须的包
- 安装特殊版本的 pip 和其他包
- 安装 Apple 提供的包(numpy, grpcio, h5py)
- 安装额外的包
- 安装 TensorFlow
- 测试
- JupyterLab
- VSCode
- 延伸阅读
- 参考
Xcode
从 App Store 安装 Xcode。

Command Line Tools
从 Apple Developer 下载安装 Xcode Command Line Tools 或者执行以下命令。
1
$ xcode-select --install
Homebrew
1
$ /bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
Miniforge
Anaconda 无法在 M1 上运行, Miniforge 是用来替代它的。
从 https://github.com/conda-forge/miniforge 下载 Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64。
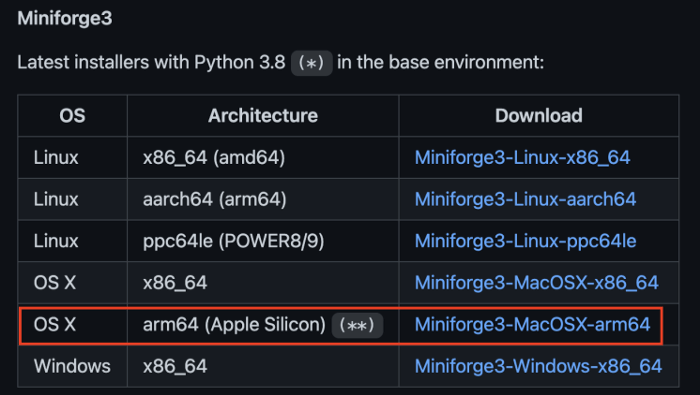
执行以下命令,安装 Miniforge
1
$ bash Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64.sh
重启终端并检查 Python 安装情况。
1
2
3
4
$ which python
/Users/catchzeng/miniforge3/bin/python
$ which pip
/Users/catchzeng/miniforge3/bin/pip
下载 Apple TensorFlow
从 https://github.com/apple/tensorflow_macos/releases 下载 TensorFlow 并解压,然后进入 arm64 目录下。
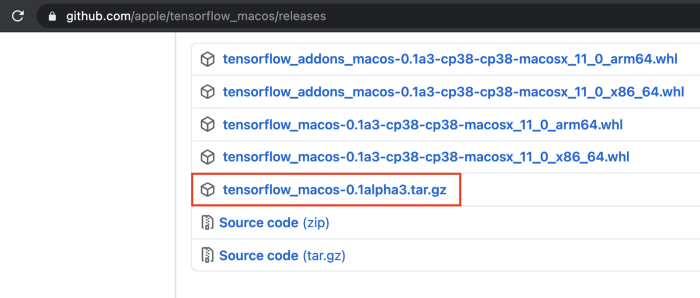
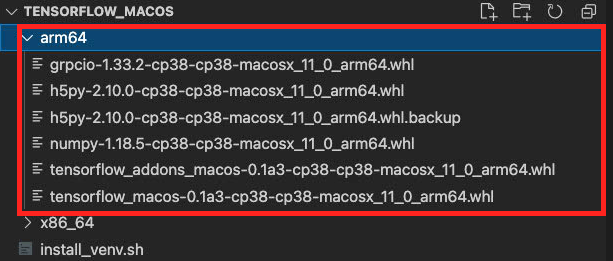
创建虚拟环境
创建一个 conda 创建虚拟环境,这里使用 python 3.8 (ATF 2.4 需要)。
1
2
$ conda create -n tensorflow python=3.8
$ conda activate tensorflow
安装必须的包
1
2
$ brew install libjpeg
$ conda install -y pandas matplotlib scikit-learn jupyterlab
注意: libjpeg 是 matplotlib 需要依赖的库。
安装特殊版本的 pip 和其他包
1
$ pip install --force pip==20.2.4 wheel setuptools cached-property six packaging
注意: Apple TensorFlow 特殊版本的 pip。
安装 Apple 提供的包(numpy, grpcio, h5py)
1
$ pip install --upgrade --no-dependencies --force numpy-1.18.5-cp38-cp38-macosx_11_0_arm64.whl grpcio-1.33.2-cp38-cp38-macosx_11_0_arm64.whl h5py-2.10.0-cp38-cp38-macosx_11_0_arm64.whl
安装额外的包
1
$ pip install absl-py astunparse flatbuffers gast google_pasta keras_preprocessing opt_einsum protobuf tensorflow_estimator termcolor typing_extensions wrapt wheel tensorboard typeguard
安装 TensorFlow
1
2
3
$ pip install --upgrade --no-dependencies --force tensorflow_macos-0.1a3-cp38-cp38-macosx_11_0_arm64.whl
$ pip install --upgrade --no-dependencies --force
tensorflow_addons_macos-0.1a3-cp38-cp38-macosx_11_0_arm64.whl
最后,升级 pip 到正确的版本。
1
$ pip install --upgrade pip
测试
TensorFlow
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
$ python
Python 3.8.8 | packaged by conda-forge | (default, Feb 20 2021, 15:50:57)
[Clang 11.0.1 ] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import tensorflow as tf
>>> print(tf.__version__)
2.4.0-rc0
>>>
JupyterLab
1
$ jupyter lab
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
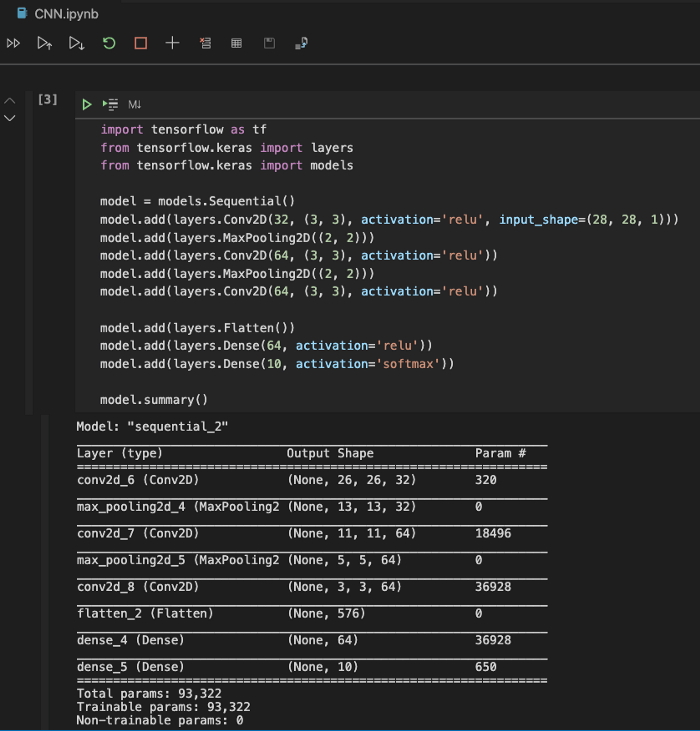
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras import models
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
model.summary()

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = mnist.load_data()
train_images = train_images.reshape((60000, 28, 28, 1))
train_images = train_images.astype('float32') / 255
test_images = test_images.reshape((10000, 28, 28, 1))
test_images = test_images.astype('float32') / 255
train_labels = to_categorical(train_labels)
test_labels = to_categorical(test_labels)
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=5, batch_size=64)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels)
test_acc

VSCode
安装 Python 支持

选择虚拟环境并信任 notebook

运行 notebook
延伸阅读
- Ubuntu 机器学习环境 (TensorFlow GPU, JupyterLab, VSCode)
- Mac 机器学习环境 (TensorFlow, JupyterLab, VSCode)
- Win10 机器学习环境 (TensorFlow GPU, JupyterLab, VSCode)
- Apple Silicon Mac M1/M2 原生支持 TensorFlow 2.10 GPU 加速(tensorflow-metal PluggableDevice)

 AI - A simple way to collect your deep learning image dataset
AI - A simple way to collect your deep learning image dataset